概述
创建PG的插件的方式分为两种,一种利用hook,一种叫Forigin Data Wrapper(FDW)。实现FDW需要实现两个C函数,Handler和 Validator (可选),然后写一个control文件。control文件是在 create extension … 的时候调用,执行相应的sql文件来建立和数据库的关联。
完成fdw的开发工作,主要的工作就是实现两个C函数,即用户自定义函数的编写,其中Handler函数的返回是一个结构体,其中包含很多函数指针,见struct FdwRoutine。外表的scan是必须要实现的方法,同时也支持了对外表的其他操作,择需而定。
关键变量:
root和baserel的信息能够减少必须要从外部表获得的信息数量,从而降低消耗。 baserel 是 RelOptInfo 类型 baserel->baserestrictinfo 是一个链表。其中都是Restrictinfo 类型, Restrictinfo类型 在pg的relation.h文件中。和sql中的WHERE和join/on相关。所以使用这个信息来过滤元素,达到优化。 如果对于一个基本表,那么会出现在基本表的baserestrictinfo中 多个表就是在joininfo中,总之就是用来过滤的。
而FDW的回调函数GetForeignRelSize, GetForeignPaths, GetForeignPlan, 和 PlanForeignModify 必须和pg的planner运行机制相符。
关键回调
1. GetForeignRelSize
void GetForeignRelSize (PlannerInfo *root,
RelOptInfo *baserel,
Oid foreigntableid);
root:查询的全局信息 baserel:查询关于这个表的信息 foreigntableid:pg_class中关于这个外部表的Oid 该函数在指定外部表扫描计划的时候调用,利用baserel->baserestrictinfo来估算好表返回的元组数,更新baserel-rows的值
GetForeignPaths
void GetForeignPaths ( PlannerInfo *root,
RelOptInfo *baserel,
Oid foreigntableid);
生成外部表扫描的路径,可能有多条路径,每条路径要有相应的cost。调用create_foreign_path来生成一个ForeignPath结构,然后add_path添加到baserel->pathlist中 ForeignPath结构如下:
typedef struct ForeignPath
{
Path path;
Path *fdw_outerpath;
List *fdw_private;
} ForeignPath;
Cstoregetforeignpath
从进程的Recache中取到foreigntableid,对应的RelationData,double check
取到查询需要的列的列表,querycolimnlist 取到该表的数据文件的块大小 relationPageCount 取到该表的关系的属性总数,relationColumnCount
由上述信息得到查询列/总列数的比值 querycolumnratio,由此估算查询的页数,从而计算磁盘数据读取代价
最终总代价由,startucost+totalcpucost+totaldiskaccessCost 最后由上述得到的信息构造一个Path,ForeignPath
GetForeignPlan
ForeignScan * GetForeignPlan ( PlannerInfo *root,
RelOptInfo *baserel,
Oid foreigntableid,
ForeignPath *best_path,
List *tlist,
List *scan_clauses,
Plan *outer_plan);
基于之前得到的path,得到ForeignScan计划,推荐函数中使用make_foreignscan来生成scanplan
void
cstoreGetForeignPaths (PlannerInfo *root,
RelOptInfo *baserel,
Oid foreigntableid);
BeginForeignScan
void BeginForeignScan (ForeignScanState *node,
int eflags);
在开始扫描之前做一些初始化的工作 注意:eflags & EXEC_FLAG_EXPLAIN_ONLY 为 true的时候,只做针对ExplainForeignScan和EndForeignScan的初始化工作。
CstoreGetforeignPlan 抽取出scanClause中的的regular clause(而不是pseudo constant clause) 只抽取需要的列,构造foreignPrivateList,这作为fdw_private
IterateForeignScan
TupleTableSlot * IterateForeignScan (
ForeignScanState *node);
每次返回一行结果,其中TupleTableSlot中可能物理tuple或者虚拟tuple,虚拟cube是为了性能提升考虑的,直接引用了底层plannode的结果,省去一次数据拷贝。
ReScanForeignScan
重新扫描,由于参数可能变化,所以重新扫描和之前可能不一样
Cstore文件结构
cstore表文件分为两部分,table footer file 和 table data file
table footer file
/*
* StripeMetadata represents information about a stripe. This information is
* stored in the cstore file's footer.
*/
typedef struct StripeMetadata
{
uint64 fileOffset;
uint64 skipListLength;
uint64 dataLength;
uint64 footerLength;
} StripeMetadata;
/* TableFooter represents the footer of a cstore file. */
typedef struct TableFooter
{
List *stripeMetadataList;
uint64 blockRowCount;
} TableFooter;
其中存有stripeMetadataList,就是table data 文件中各个stripe的元信息; 每个stripe分为三部分: stripe skip list column data stripe footer 。 元信息中存下了每个stripe在文件中的偏移,以及各部分的长度,便于读取各个部分的信息。
table data file
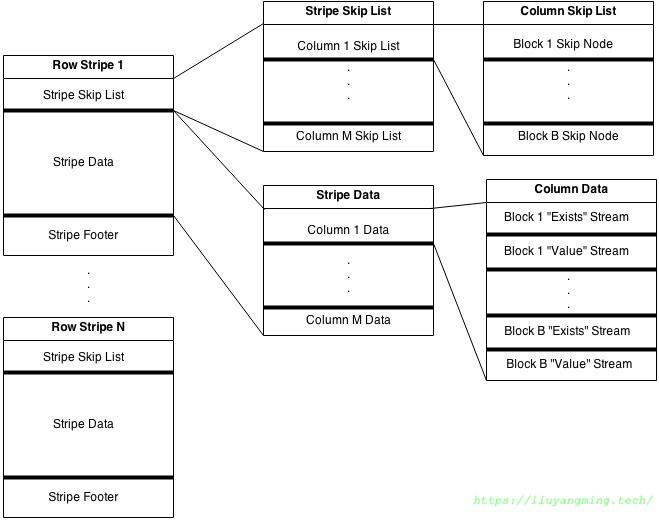 其由很多stripe构成; 每个stripe中是按列存放的, 每列数据包括exists序列、 value序列 物理上,exists序列是连续存放的,同样,value序列也是连续存放的,放在exists后面;
其由很多stripe构成; 每个stripe中是按列存放的, 每列数据包括exists序列、 value序列 物理上,exists序列是连续存放的,同样,value序列也是连续存放的,放在exists后面;
逻辑上,exists和value都分成若干块,由于每个block中的rowcount不能超过在table footer中定义blockrowcount的大小,所以逻辑上每列分成相同几块,columndata就像是一个二维数组,二维数组的某个元素就是某一列的某一块(这里的block不是磁盘上的block)。
/*
* StripeSkipList can be used for skipping row blocks. It contains a column block
* skip node for each block of each column. blockSkipNodeArray[column][block]
* is the entry for the specified column block.
*/
typedef struct StripeSkipList
{
ColumnBlockSkipNode **blockSkipNodeArray;
uint32 columnCount;
uint32 blockCount;
} StripeSkipList;
每个stripe都有一个stripe skip list,其中有一个二维的数组: blockskipnodearray[][] blockskipnodearray[ci][bi] 便是第ci列的第bi块的信息,其中有该块的列是否有最大最小值,最大最小值是什么,该块有多少行,该块的exist序列在整个的exists序列中的偏移及长度,该块的value序列在整个的value序列中的偏移及长度,压缩类型
/*
* StripeSkipList can be used for skipping row blocks. It contains a column block
* skip node for each block of each column. blockSkipNodeArray[column][block]
* is the entry for the specified column block.
*/
typedef struct StripeSkipList
{
ColumnBlockSkipNode **blockSkipNodeArray;
uint32 columnCount;
uint32 blockCount;
} StripeSkipList;
每次读取一个stripe的时候,首先读取stripe footer,其中包含三个数组,长度就是columncount, 分别存有每列的skip list size, exist序列的size,value序列的size.
Cstore的读取写入
读取
读取数据首先先读取 table footer中的信息,信息存入readstate,readstate记录了当前读到哪个stripe了,以及一个stripebuffer, stripe buffer 就是已经用 project column 和 where clause 将column data过滤过了。(将一个大的二维数组过滤成一个小的二维数组,project column将不用的列过滤掉,where clause将不用的行过滤掉。) 每次需要返回的一行数据时,从stripebuffer中读取一行数据,对于已经过滤掉的列,就被设置成null了。
写入
writestate中维护了一个当前正在写的stripe,当我们要写入行数据时,添加到当前的stripe中,在每列数据后追加,同时更新相应的skip node,当每个block写满后,这整个block就被压缩,然后,如果总的行数达到stripemaxrowcount,就将这个stripe写盘,更新table footer中的元信息
Foreign data wrapper
使用FDW
在contrib中,自带一些fdw;
或者 https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/Foreign_data_wrappers
- make && make install ,讲相应配置文件和库文件拷贝到PG的lib目录,
- create extension … 加载这个插件
编写FDW
- 实现两个C函数,Handler和 Validator (可选)。
- 然后写一个control文件,control文件是在create extension加载的文件,根据这个文件,PG去寻找对应的sql文件,在 create extension … 的时候,执行相应的sql文件,来建立和数据库的关联。
- 配置好上述 control文件和sql文件后,按照fdw的函数模板,编写动态链接库,即FDW插件。
Handler
handler中是很多函数指针,用来匹配PG中执行计划执行。对于外表的scan是必须要实现的方法,同时也支持了对外表的其他操作,择需而定。
fdw的回调函数GetForeignRelSize, GetForeignPaths, GetForeignPlan, PlanForeignModify 必须和pg的planner运行机制相符。
关键函数
GetForeignRelSize
void GetForeignRelSize (PlannerInfo *root,
RelOptInfo *baserel,
Oid foreigntableid);
root:查询的全局信息 baserel:查询关于这个表的信息 foreigntableid:pg_class中关于这个外部表的Oid 该函数在制定外部表扫描计划的时候调用,利用baserel->baserestrictinfo来估算好表返回的元组数,更新baserel->rows的值
GetForeignPaths
void GetForeignPaths ( PlannerInfo *root,
RelOptInfo *baserel,
Oid foreigntableid);
生成外部表扫描的路径,可能有多条路径,每条路径要有相应的cost。从进程的Recache中取到foreigntableid,对应的RelationData,double check
取到查询需要的列的列表,querycolimnlist 取到该表的数据文件的块大小 relationPageCount 取到该表的关系的属性总数,relationColumnCount
由上述信息得到查询列/总列数的比值 querycolumnratio,由此估算查询的页数,从而计算磁盘数据读取代价
最终总代价由,startucost+totalcpucost+totaldiskaccessCost 最后由上述得到的信息构造一个Path,ForeignPath
GetForeignPlan
ForeignScan * GetForeignPlan ( PlannerInfo *root,
RelOptInfo *baserel,
Oid foreigntableid,
ForeignPath *best_path,
List *tlist,
List *scan_clauses,
Plan *outer_plan);
基于之前得到的path,得到ForeignScan计划。
BeginForeignScan
void BeginForeignScan (ForeignScanState *node,
int eflags);
在开始扫描之前做一些初始化的工作 注意:eflags & EXEC_FLAG_EXPLAIN_ONLY 为 true的时候,只做针对ExplainForeignScan和EndForeignScan的初始化工作。
IterateForeignScan
TupleTableSlot * IterateForeignScan (
ForeignScanState *node);
每次返回一行结果,其中TupleTableSlot中可能物理tuple或者虚拟tuple,虚拟cube是为了性能提升考虑的,直接引用了底层plannode的结果,省去一次数据拷贝。
ReScanForeignScan
重新扫描,由于参数可能变化,所以重新扫描和之前可能不一样